本文共 9137 字,大约阅读时间需要 30 分钟。
dijkstra + 堆优化 + 链式前向星存图 + 枚举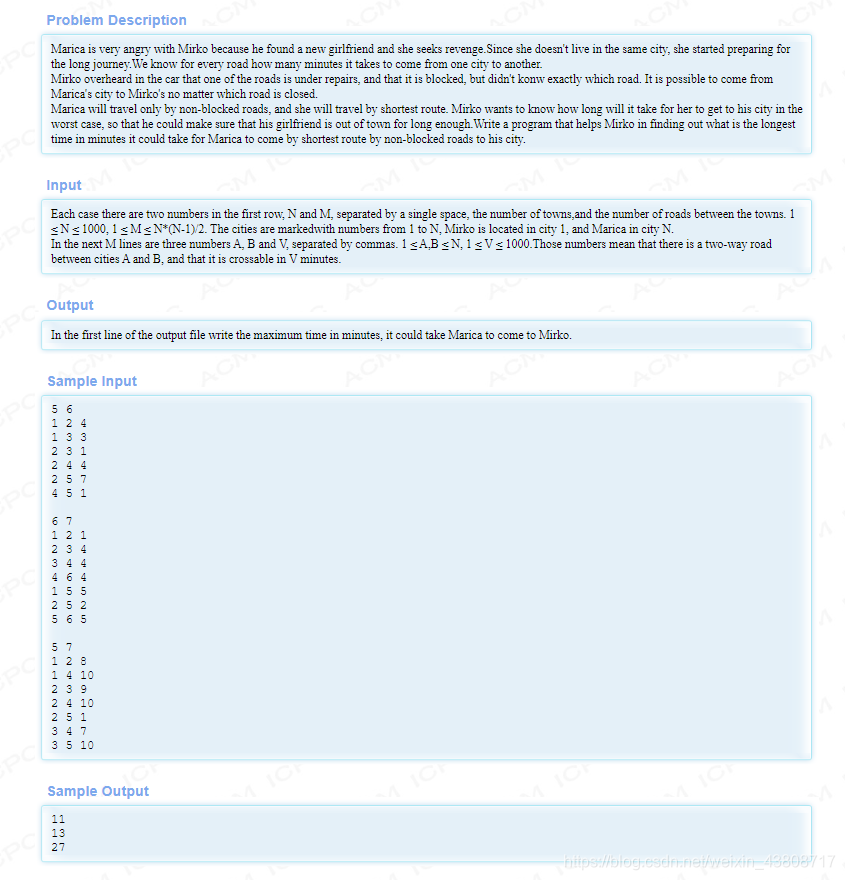 大概题意:从1到n点如果切掉一条路,那么在最坏情况下的最短路是多少。
大概题意:从1到n点如果切掉一条路,那么在最坏情况下的最短路是多少。 题目思路:开始做的时候是暴力枚举所有的边进行标记,然后分别跑一次dijkstra算当前情况下的最短路。然后在这些最短路里面找一个最大的就是答案。然后码完一交TLE,其实做之前就算了一下复杂度我知道要超时但是还是忍不住要试一下,毕竟人要勇敢一点嘛~~~因为最短路是经过一定的边数的,很多边我们是不走的,所以删掉这些不走的边并不会影响我们的最短路,换句话说就是删掉这些不走的边跑出来的最短路答案和没删边之前答案一样。所以我们就聪明一点,枚举最短路上的所有边,分别进行一次删除,再来求最短路。这样我们是不是减少了大量无用的枚举,自然dijkstra就少跑了很多次!!!当然这道题也能spfa做,但是我想说一句年轻人少做spa~
//注意这是无向图,链式前向星存图边数应该再加一倍#include#include #include #include #include using namespace std;const int inf = 1<<30;const int maxm = 1e6;const int maxn = 1006;struct edge{ int to; int w; int next;}e[maxm];struct info{ int k,s; info(int a,int b){ k = a;s = b; } bool operator <(const info a)const{ return a.s < s; }};int head[maxm]; //链式前向星头结点int cnt;int id[maxm]; //最短路上经过的边的序号priority_queue q;int dist[maxn]; //距离数组bool visited[maxn]; //标记数组int pre[maxn]; //前驱数组inline void addedge(int x,int y,int w){ e[cnt].to = y; e[cnt].w = w; e[cnt].next = head[x]; head[x] = cnt++;}inline void clear_set(){ memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); fill(dist,dist+maxn,inf); while(!q.empty()){ q.pop(); }}inline void new_set(){ cnt = 0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); //链式前向星头结点初始化 memset(id,0,sizeof(id)); //最短路径上的边的编号 memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre)); //前驱节点初始化 }int dijkstra(int flag,int n){ clear_set(); dist[1] = 0; q.push(info(1,0)); while(!q.empty()){ info p = q.top(); q.pop(); if(visited[p.k]){ continue; } visited[p.k] = true; for(int i = head[p.k];i != -1;i = e[i].next){ //head[p.k]访问的是边的编号 edge t = e[i]; if(!visited[t.to] && dist[t.to] > dist[p.k] + t.w){ //松弛 dist[t.to] = dist[p.k] + t.w; q.push(info(t.to,dist[t.to])); if(flag == 1){ pre[t.to] = p.k; //记录前驱节点 id[t.to] = i; //记录到达这个点的边的序号 } } } } if(dist[n] == inf){ return -1; } return dist[n];}int main(){ int n,m; while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)){ new_set(); for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ int x,y,z; scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); addedge(x,y,z); addedge(y,x,z); } int ans = dijkstra(1,n); int t = n; while(t != -1){ //枚举最短路经过的所有边,分别进行一次"删除" int w = e[id[t]].w; e[id[t]].w = inf; ans = max(ans,dijkstra(0,n)); e[id[t]].w = w; t = pre[t]; } printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0;}
这道题好像没有重边可以用邻接矩阵存图,建议还是学一个通用的做法,用链式前向星存图
这两道题一个意思,下面贴一个dijkstra 和 spfa解法的模板。其实这两个算法说来说去都差不多,dijkstra的优势就是贪心,稳定。spfa不稳定,业界卡spfa已经成习惯了,别跟我扯什么spfa优化,你就是没有dijkstra稳定,挨打要站稳!spfa的优势就是能判负环圈,做最长路,做差分约束好。
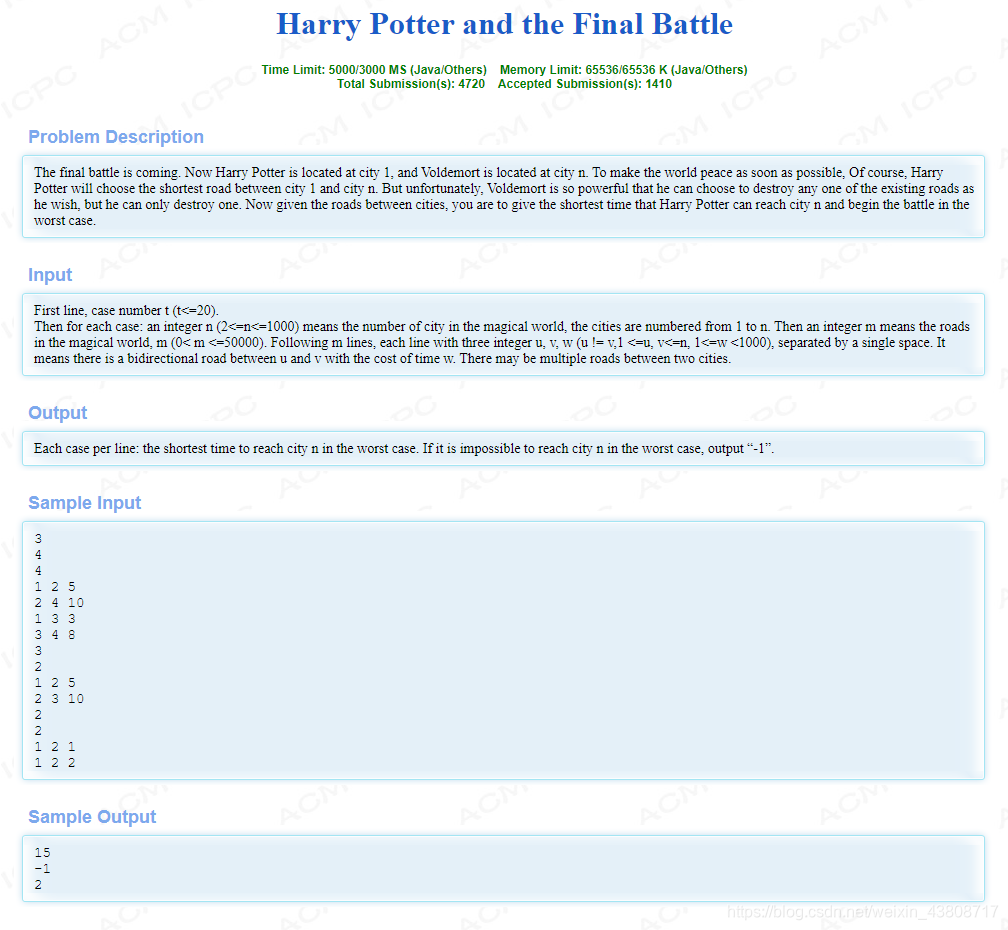
//dijkstra Accepted 3986 327MS 2600K 2434B//spfa Accepted 3986 405MS 2596K 2381B#include#include #include #include #include using namespace std;const int inf = 1<<30;const int maxn = 1005;const int maxm = 1e6;struct edge{ int to; int w; int next;}e[maxm];struct info{ int k,s; info(int a,int b){ k = a;s = b; } bool operator<(const info a)const{ return a.s < s; }}; int head[maxn];int dist[maxn];int pre[maxn];int num[maxn];bool visited[maxn];int n,m,cnt;priority_queue q;//queue q;inline void addedge(int x,int y,int z){ e[cnt].to = y; e[cnt].w = z; e[cnt].next = head[x]; head[x] = cnt++;}inline void new_set(){ cnt = 0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre)); memset(num,0,sizeof(num));}inline void clear_set(){ memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); fill(dist,dist+maxn,inf); while(!q.empty()){ q.pop(); }}/*int spfa(int flag){ clear_set(); dist[1] = 0; visited[1] = true; q.push(1); while(!q.empty()){ int p = q.front(); q.pop(); visited[p] = false; for(int i = head[p];i != -1;i = e[i].next){ edge t = e[i]; if(dist[t.to] > dist[p] + t.w){ dist[t.to] = dist[p] + t.w; if(flag){ pre[t.to] = p; num[t.to] = i; } if(!visited[t.to]){ q.push(t.to); visited[t.to] = true; } } } } return dist[n];}*/int dijkstra(int flag){ clear_set(); dist[1] = 0; q.push(info(1,0)); while(!q.empty()){ info p = q.top(); q.pop(); if(visited[p.k]){ continue; } visited[p.k] = true; for(int i = head[p.k];i != -1;i = e[i].next){ edge t = e[i]; if(!visited[t.to] && dist[t.to] > dist[p.k] + t.w){ dist[t.to] = dist[p.k] + t.w; q.push(info(t.to,dist[t.to])); if(flag){ pre[t.to] = p.k; num[t.to] = i; } } } } return dist[n];}int main(){ int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--){ new_set(); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ int x,y,z; scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); addedge(x,y,z); addedge(y,x,z); } // int ans = spfa(1); int ans = dijkstra(1); int k = n; while(k != -1){ int w = e[num[k]].w; e[num[k]].w = inf; //该边不通 // ans = max(ans,spfa(0)); ans = max(ans,dijkstra(0)); e[num[k]].w = w; k = pre[k]; } if(ans == inf){ ans = -1; } printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0;}
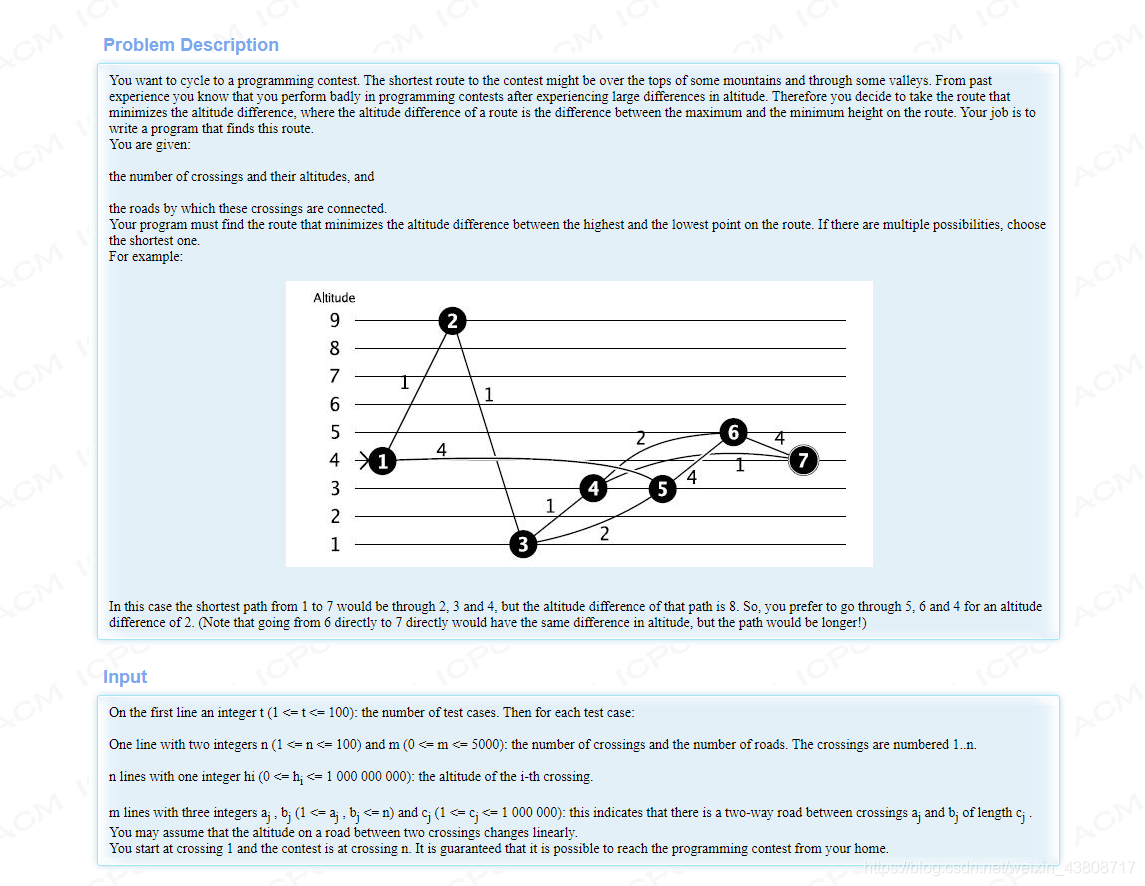
题意:从1-n点求最短路,不过这个最短路中引入了高度差的概念,保证两点高度差最小的情况下的最短路,没有高度差的时候最短路是从1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 7最短路是4,高度差是height[2] - height[3] = 8;
思路:枚举,计算任意两点之间的高度差,按照从小到大排序好,然后枚举每一种高度差的情况去跑dijkstra或者spfa,中途经过的点要去判断该点在不在最大高度和最小高度之间,如果在才能更新,一旦在这个高度差能够到达终点直接退出枚举。题目小坑的地方在于存在起点和终点相同的情况,WA了好几发才发现。
#include题意:一个无向图中,求从s - t的最短路,前提是s - t的高度尽量大。说白了就是s - t要求高度尽量最大下的最短路。#include #include #include #include using namespace std;const int inf = 1<<30;const int maxn = 105;const int maxm = 10005;struct info{ int x; //最小高度 int y; //最大高度 }s[maxm];struct edge{ int to; //边终点 int w; //边权重 int next; //下一条边 }e[maxm];struct Node{ int k,s; Node(int a,int b){ k = a;s = b; } bool operator <(const Node a)const{ return a.s < s; }};priority_queue q;int cnt,n,m;int head[maxn];int height[maxn];int visited[maxn];int dist[maxn]; inline void addedge(int x,int y,int z){ e[cnt].to = y; e[cnt].w = z; e[cnt].next = head[x]; head[x] = cnt++;}inline void new_set(){ cnt = 0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); memset(height,0,sizeof(height));}inline void clear_set(){ memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); fill(dist,dist+maxn,inf); while(!q.empty()){ q.pop(); }}bool cmp(info a,info b){ return (a.y - a.x) < (b.y - b.x); //高度差从小到大 }int dijkstra(int x,int y){ clear_set(); dist[1] = 0; q.push(Node(1,0)); while(!q.empty()){ Node p = q.top(); q.pop(); //判断该点是否松弛过,并且是不是在这个高度允许的范围内 if(visited[p.k] || height[p.k] < x || height[p.k] > y){ continue; } visited[p.k] = true; for(int i = head[p.k];i != -1;i = e[i].next){ edge t = e[i]; //同上 if(visited[t.to] || height[t.to] < x || height[t.to] > y){ continue; } if(dist[t.to] > dist[p.k] + t.w){ dist[t.to] = dist[p.k] + t.w; q.push(Node(t.to,dist[t.to])); } } } if(dist[n] == inf){ //没有找到 return -1; } return dist[n];}int main(){ int t; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--){ new_set(); scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){ //建议利用一下数组下标不要从0开始 scanf("%d",&height[i]); } for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ int x,y,z; scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); addedge(x,y,z);addedge(y,x,z); //加入无向边 } int cnt = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++){ for(int j = i;j <= n;j++){ //有起点和终点相同的情况,小坑 if(height[i] > height[j]){ s[cnt].x = height[j]; s[cnt].y = height[i]; } else{ s[cnt].x = height[i]; s[cnt].y = height[j]; } cnt++; } } sort(s,s+cnt,cmp); //排序 for(int i = 0;i < cnt;i++){ int ans = dijkstra(s[i].x,s[i].y); if(ans != -1){ //找到解直接打印退出 printf("%d %d\n",s[i].y-s[i].x,ans); break; } } } return 0;}
题解:从大到小依次枚举高度或者二分枚举高度,再去跑dijkstra或者spfa,松弛的时候判断一下这条边的高度限制是不是低于当前允许的最大高度,低于的话就跳过不进行松弛。
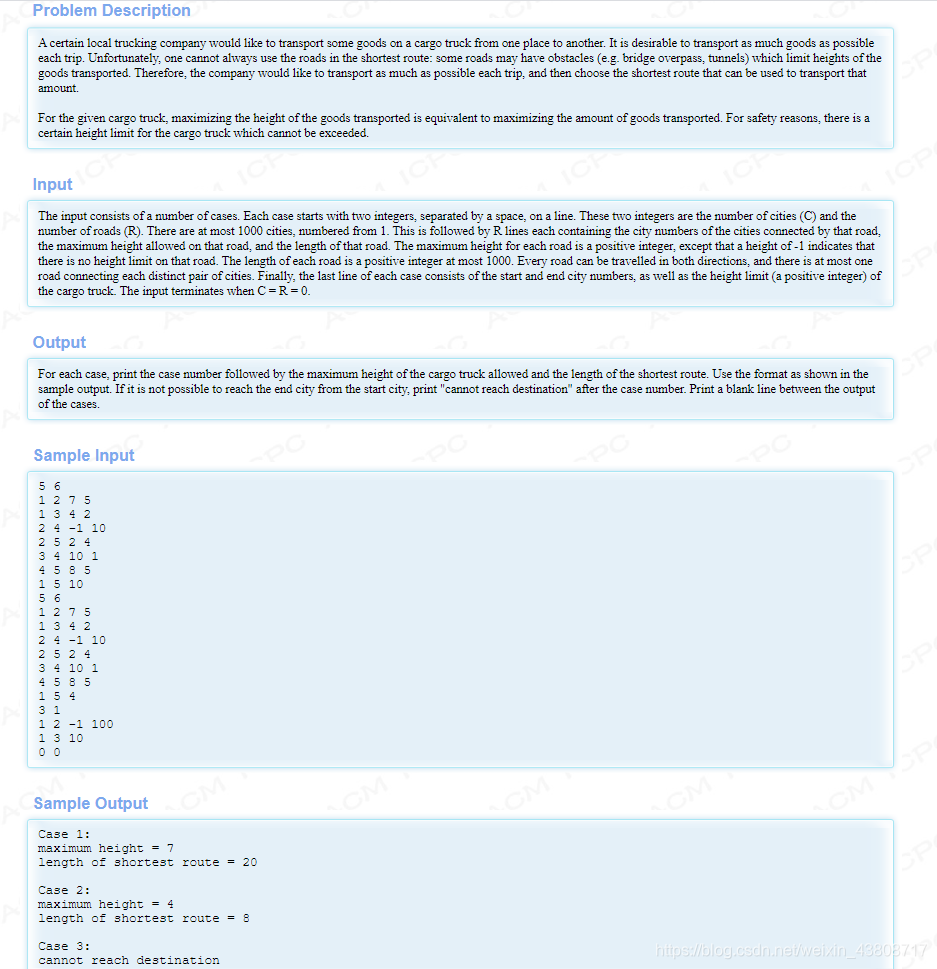
//二分枚举代码,也可以暴力枚举从最大高度开始枚举。#include#include #include #include #include #include #include using namespace std;const int maxn = 1005;const int inf = 1<<31-1;const int maxm = 1e6+1e4;struct edge{ int to; int w; int h; int next;}e[maxm];struct Node{ int k,s; Node(int a,int b){ k = a;s = b; } bool operator <(const Node a)const{ return a.s < s; }};priority_queue q;int cnt,n,m;int head[maxn];int dist[maxn];bool visited[maxn];inline void new_set(){ cnt = 0; memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));}inline void clear_set(){ memset(visited,false,sizeof(visited)); fill(dist,dist+maxn,inf); while(!q.empty()){ q.pop(); }}inline void addedge(int x,int y,int z,int c){ e[cnt].to = y; e[cnt].w = z; e[cnt].h = c; e[cnt].next = head[x]; head[x] = cnt++;}bool cmp(int x,int y){ return x > y;}int dijkstra(int s,int t,int x){ clear_set(); dist[s] = 0; q.push(Node(s,0)); while(!q.empty()){ Node p = q.top(); q.pop(); if(visited[p.k]){ continue; } visited[p.k] = true; for(int i = head[p.k];i != -1;i = e[i].next){ edge f = e[i]; if(visited[f.to]){ continue; } if(f.h != -1 && f.h < x){ continue; } if(dist[f.to] > dist[p.k] + f.w){ dist[f.to] = dist[p.k] + f.w; q.push(Node(f.to,dist[f.to])); } } } return dist[t];} int main() { int k = 1; while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&m) && n && m){ new_set(); int x,y,c,z; for(int i = 0;i < m;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&c,&z); addedge(x,y,z,c);addedge(y,x,z,c); } scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); int index = 0,res = inf; int l = 0,r = z; while(l <= r){ int mid = (l+r)>>1; int ans = dijkstra(x,y,mid); if(ans != inf){ if(mid > index){ index = mid; res = ans; } l = mid+1; } else{ r = mid-1; } } if(k != 1){ printf("\n"); } printf("Case %d:\n",k); if(res != inf){ printf("maximum height = %d\n",index); printf("length of shortest route = %d\n",res); } else{ printf("cannot reach destination\n"); } k++; } return 0;}
不定时更新~
转载地址:http://thep.baihongyu.com/